Blog
5G vs 4G: What Makes 5G Better?
August 17, 2023 — by NICHOLAS JONES
SHARE ARTICLE[Sassy_Social_Share total_shares="ON"]
With 5G on the horizon, here’s what you can expect from 5G vs 4G.
What is 5G?
In broad terms, 5G is the planned successor to 4G. If you’re wondering exactly what that means, let’s break it down further.
The G in 5G stands for generation. Essentially, 5G represents the fifth and latest generation of mobile communication networks. Also known as cellular networks, they’re used to transmit voice and data for smart phones and mobile devices.
Moreover, 5G isn’t one single identifiable thing. It’s a variety of technologies coming together to speed up cellular communication and enable more devices to connect to the internet than ever before.
Advantages of 5G over 4G
What distinguishes 5G vs 4G and earlier predecessors is that it’s designed for a constantly connected world. In fact, this may be the first generation of mobile communications technology designed specifically with industry, enterprise, and the Internet of Things (IoT) in mind.

5G is meant to connect people and things in networked environments, enabling smart homes, smart cities, cloud applications, remote medical services, and the machine-to-machine communication that’s required for efficient, accurate automation. Because of this, 5G may be a game changer for many industries and emerging technologies.
There are several things that make 5G advantageous:
- Faster speed
- Very low latency
- Greater reliability
- Overall better user experience
To better understand the potential advantages and disadvantages of 5G vs 4G, it’s helpful to break it down into several main components.
5G vs 4G: speed
One of the main benefits of 5G is its exceptional speed. So, just how much faster is 5G vs 4G?
According to the FCC, this next-generation network of mobile communications technology can download data up to 100 times faster than 4G, resulting in nearly instantaneous response times. For example, a movie that would take six minutes to download using 4G could be downloaded in as few as 15 seconds using 5G. That’s a huge difference when you’re waiting for a download to finish.
In more specific terms, 4G technology supports downloads at speeds of approximately 12 to 36 megabits per second (Mbps). 5G, on the other hand, should support a rate of 300 Mbps or more.
Download speeds aren’t the only consideration when it comes to the rate of transfer. Although many network providers are still not talking much about 5G upload speeds, users can plan on a 30% or higher increase in overall upload speed. That brings it to between 25 and 100 Mbps.
This increase in upload speed can mean a significant boost in efficiency for anyone backing up files or uploading large videos. It may also result in increased productivity for individuals working at home.
When comparing 5G vs. 4G speeds, it’s important to remember that rates may vary, and speeds are dependent on factors beyond network capabilities. Other factors that affect the rate of transfer include:
- The device you’re using
- The network you’re connecting to
- The number of users on the network at the time
- Your location
These factors can contribute to something called latency.
5G vs 4G: latency
Network latency may be more practical than speed as a measure of the advantage of 5G, since it refers to the amount of time data takes to move from one point to another. In other words, latency is the span between when your device sends data and the device on the other end receives it.
Several main factors play into latency, including:
- The network’s speed
- Available bandwidth
- The size of the data being transmitted
With 5G, users should be able to transmit data — even large files — in real-time. This is not only beneficial to busy, on-the-go users, but it can have important applications for public safety, providing critical information in the blink of an eye to emergency services and other first responders.
5G vs 4G: frequency
5G uses higher frequency waves than 4G, taking advantage of wavelengths that were previously unavailable due to high costs and government restrictions. These higher frequencies are what enable the technology to achieve greater speeds.
However, there is a downside. These high-frequency waves don’t penetrate objects as well as those used in 4G, which can pose challenges for indoor use, mountainous areas, and cities where signals may need to travel through buildings.
This barrier to service presents significant challenges for carriers, as it may require customers to have special equipment to facilitate service, including signal boosters in large public venues, (such as conference centers and shopping malls), homes or apartment buildings, and even vehicles, at least until the full infrastructure is eventually rolled out.
5G vs 4G: distance
The move to higher frequency waves has led many consumers to ask: is 5G a stronger signal than 4G? The question isn’t an easy one to answer, since comparing signal strength between 4G and 5G is a bit like comparing apples to oranges. Plus, it’s reliant on the location you’re transmitting from.
Unfortunately, the high-frequency wavelengths of 5G generally do lead to a much shorter range due to the difficulties with object penetration. However, later rollouts will likely use lower, sub-6 GHz bands, which provide a wider range and should travel farther.
So, can 5G penetrate walls? Well, not exactly. In fact, many of the wavelengths used for next-generation mobile communications not only can’t penetrate walls; they also can’t penetrate glass, human bodies, or even small objects, such as leaves. Even when there aren’t physical obstacles, these waves are easily absorbed by air, drastically cutting down the distance they can travel.
The distance 5G can travel will ultimately depend on where it’s deployed and the exact frequency of the network involved. Because 5G signals are more easily interrupted, the coverage area of a 5G cell site is measured in feet instead of miles. Because of its limited range, 5G won’t immediately replace 4G LTE everywhere, but in metropolitan cities where 5G cell sites (or nodes) are more concentrated, lightning-fast 5G speeds should be a reality much sooner.
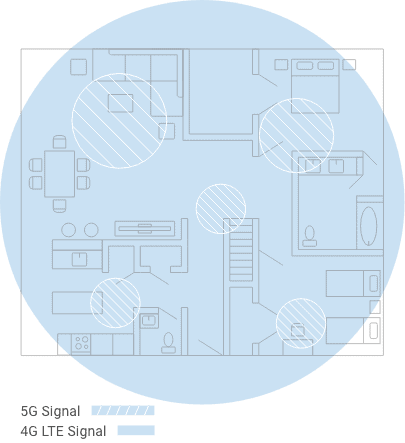
5G vs 4G: technology considerations
Whether 5G truly represents a new generation of mobile communications or is just an enhanced version of 4G, the leap forward means change for cell phone users. Although the ongoing 5G rollout won’t make 4G phones immediately obsolete, you will need a new 5G-compatible cell phone to take advantage of the technology as it becomes commercially available.
Some providers may also begin to phase out the older 3G technology, so if you’ve been holding onto a device that was designed for 3G, you may need to invest in that upgrade sooner than later.
How weBoost can significantly improve the performance of 5G
The emerging 5G technology combines existing network bands with new bands to achieve a wider spectrum. Our cell phone signal boosters can significantly improve this technology by strengthening the signal, resulting in stronger cellular coverage.
A cell phone signal booster can improve voice quality, increase data transfer speeds, and reduce the number of dropped calls whether you’re in your home or on the road. We also offer units that can accommodate larger commercial spaces.
Cell phone boosters can be used regardless of which US carrier network you use. Using interior and exterior antennas, some home boosters are capable of supporting multiple users and multiple devices in the same household, even when the structure has more than one level.
Cell phone signal boosters offer an array of benefits, including:
- Fewer dead zones
 Longer battery life on mobile devices
Longer battery life on mobile devices- Larger indoor coverage range
- Less dependence on Wi-Fi
- Increased use of your unlimited data plan
- Improved video streaming
- Improved hotspot functionality
Find out more about how weBoost can help you boost your cell phone signal at home or on the road. Contact us online or give us a call at 1-866-294-1660.
buttonbutton SHARE ARTICLE[Sassy_Social_Share total_shares="ON"]TAGS: 5G

